- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
I'm suggest to personally of all student , those student interest or prepare any VIVA in computer networking , So please read and view this question to carefully.
This question will help a lot. if you given any VIVA and interview bases of computer networking.
Most important 20 question for computer networking
Content
- What is a Network?
- What is a Node?
- What is Network Topology?
- What are Routers?
- What is the difference between Hub, Switch, and Router?
- Explain TCP/IP Model
- What is HTTP and what port does it use?
- What is HTTPs and what port does it use?
- What are TCP and UDP?
- What is a Firewall?
- What is DNS?
- What are IP classes and how can you identify the IP class of given an IP address?
- What is NIC?
- What are the different types of a network? Explain each briefly.
- Name the different types of network topologies and brief their advantages?
- Define Static IP and Dynamic IP?
- Define Static IP and Dynamic IP?
- What is difference between unicast broadcast and multicast?
- Difference between IPV4 VS IPV6?
- Define IP address class and range?
Q .1) What is a Network?
Answer: Network is defined as a set of devices connected to each other using a physical transmission medium.
For Example, A computer network is a group of computers connected with each other to communicate and share information and resources like hardware, data, and software. In a network, nodes are used to connect two or more networks.
Q .2) What is a Node?
Answer: Two or more computers are connected directly by an optical fiber or any other cable. A node is a point where a connection is established. It is a network component that is used to send, receive and forward the electronic information.
A device connected to a network is also termed as Node. Let’s consider that in a network there are 2 computers, 2 printers, and a server are connected, then we can say that there are five nodes on the network.
Q .3) What is Network Topology?
Answer: Network topology is a physical layout of the computer network and it defines how the computers, devices, cables, etc are connected to each other.
Q .4) What are Routers?
Answer: The router is a network device that connects two or more network segments. It is used to transfer information from the source to the destination.
Routers send the information in terms of data packets and when these data packets are forwarded from one router to another router then the router reads the network address in the packets and identifies the destination network.
Q .5) What is the difference between Hub, Switch, and Router?
Answer:
Hub
- Hub is least expensive, least intelligent and least complicated of the three.
- It broadcast all data to every port which may cause serious security and reliability concern
- In a Network, Hub is a common connection point for devices connected to the network. Hub contains multiple ports and is used to connect segments of LAN
Switch
- Switches work similarly like Hubs but in a more efficient manner.
- It creates connections dynamically and provides information only to the requesting port
- Switch is a device in a network which forwards packets in a network
Router
- The router is smartest and most complicated out of these three. It comes in all shapes and sizes. Routers are similar like little computers dedicated for routing network traffic
- Routers are located at gateway and forwards data packets
Q. 6) Explain TCP/IP Model?
Answer: The most widely used and available protocol is TCP/IP i.e. Transmission Control Protocol and Internet Protocol. TCP/IP specifies how data should be packaged, transmitted and routed in their end to end data communication.
There are four layers as shown in the below diagram:
Given below is a brief explanation of each layer:
Application Layer:
This is the top layer in the TCP/IP model.
It includes processes that use the Transport Layer Protocol to transmit the data to their destination. There are different Application Layer Protocols such as HTTP, FTP, SMTP, SNMP protocols, etc.
Transport Layer:
It receives the data from the Application Layer which is above the Transport Layer. It acts as a backbone between the host’s system connected with each other and it mainly concerns about the transmission of data. TCP and UDP are mainly used as Transport Layer protocols.
Network or Internet Layer:
This layer sends the packets across the network. Packets mainly contain source & destination IP addresses and actual data to be transmitted.
Network Interface Layer:
It is the lowest layer of the TCP/IP model. It transfers the packets between different hosts. includes encapsulation of IP packets into frames, mapping IP addresses to physical hardwar devices, etc.
Q.7) What is HTTP and what port does it use?
Answer: HTTP is HyperText Transfer Protocol and it is responsible for web content. Many web pages are using HTTP to transmit the web content and allow the display and navigation of HyperText. It is the primary protocol and port used here is TCP port 80.
Q.8) What is HTTPs and what port does it use?
Answer: HTTPs is a Secure HTTP. HTTPs is used for secure communication over a computer network. HTTPs provides authentication of websites that prevents unwanted attacks.
In bi-directional communication, the HTTPs protocol encrypts the communication so that the tampering of the data gets avoided. With the help of an SSL certificate, it verifies if the requested server connection is a valid connection or not. HTTPs use TCP with port 443.
Q .9) What are TCP and UDP?
Answer: Common factors in TCP and UDP are:
TCP and UDP are the most widely used protocols that are built on the top of the IP protocol.
Both protocols TCP and UDP are used to send bits of data over the Internet, which is also known as ‘packets’.
When packets are transferred using either TCP or UDP, it is sent to an IP address. These packets are traversed through routers to the destination.
The difference between TCP and UDP are enlisted in the below table:
TCP
- TCP stands for Transmission Control Protocol
- Once the connection is setup, data can be sent bi-directional i.e. TCP is a connection oriented protocol
- The speed of TCP is slower than UDP
- TCP is used for the application where time is not critical part of data transmission
- TCP transmission occurs in a sequential manner
- It is heavy weight connection
- TCP tracks the data sent to ensure no data loss during data transmission
UDP
- UDP is stands for User Datagram Protocol or Universal Datagram Protocol
- UDP is connectionless, simple protocol. Using UDP, messages are sent as packets.
- UDP is faster compared to TCP
- UDP is suitable for the applications which require fast transmission of data and time is crucial in this case.
- UDP transmission also occurs in a sequential manner but it does not maintain the same sequence when it reaches the destination.
- It is lightweight transport layer
- UDP does not ensure whether receiver receives packets are not. If packets are misses then they are just lost.
Q .10) What is a Firewall?
Answer: Firewall is a network security system that is used to protect computer networks from unauthorized access. It prevents malicious access from outside to the computer network. A firewall can also be built to grant limited access to outside users.
The firewall consists of a hardware device, software program or a combined configuration of both. All the messages that route through the firewall are examined by specific security criteria and the messages which meet the criteria are successfully traversed through the network or else those messages are blocked.
Firewalls can be installed just like any other computer software and later can be customized as per the need and have some control over the access and security features. “
Windows Firewall” is an inbuilt Microsoft Windows application that comes along with the operating system. This “Windows Firewall” also helps to prevent viruses, worms, etc.
Q .11) What is DNS?
Answer: Domain Name Server (DNS), in a non-professional language and we can call it an Internet’s phone book. All the public IP addresses and their hostnames are stored in the DNS and later it translates into a corresponding IP address.
For a human being, it is easy to remember and recognize the domain name, however, the computer is a machine that does not understand the human language and they only understand the language of IP addresses for data transfer.
There is a “Central Registry” where all the domain names are stored and it gets updated on a periodic basis. All Internet service providers and different host companies usually interact with this central registry to get the updated DNS details.
For Example, When you type a website www.softwaretestinghelp.com, then your Internet service provider looks for the DNS associated with this domain name and translates this website command into a machine language – IP address – 151.144.210.59 (note that, this is the imaginary IP address and not the actual IP for the given website) so that you will get redirected to the appropriate destination.
This process is explained in the below diagram:

Q .12) What are IP classes and how can you identify the IP class of given an IP address?
Answer: An IP address has 4 sets (octets) of numbers each with a value up to 255.
For Example, the range of the home or commercial connection started primarily between 190 x or 10 x. IP classes are differentiated based on the number of hosts it supports on a single network. If IP classes support more networks then very few IP addresses are available for each network.
There are three types of IP classes and are based on the first octet of IP addresses which are classified as Class A, B or C. If the first octet begins with 0 bit then it is of type Class A.
Class A type has a range up to 127.x.x.x (except 127.0.0.1). If it starts with bits 10 then it belongs to Class B. Class B having a range from 128.x to 191.x. IP class belongs to Class C if the octet starts with bits 110. Class C has a range from 192.x to 223.x.
Q .13) What is NIC?
Answer: NIC stands for Network Interface Card. It is also known as Network Adapter or Ethernet Card. It is in the form of an add-in card and is installed on a computer so that the computer can be connected to a network.
Q .14) What are the different types of a network? Explain each briefly.
Answer: There are 4 major types of networks.
Let’s take a look at each of them in detail.
- Personal Area Network (PAN): It is the smallest and basic network type that is often used at home. It is a connection between the computer and another device such as phone, printer, modem tablets, etc
- Local Area Network (LAN): LAN is used in small offices and Internet cafes to connect a small group of computers to each other. Usually, they are used to transfer a file or for playing the game in a network.
- Metropolitan Area Network (MAN): It is a powerful network type than LAN. The area covered by MAN is a small town, city, etc. A huge server is used to cover such a large span of area for connection.
- Wide Area Network (WAN): It is more complex than LAN and covers a large span of the area typically a large physical distance. The Internet is the largest WAN which is spread across the world. WAN is not owned by any single organization but it has distributed ownership.
There are some other types of the network as well:
- Storage Area Network (SAN)
- System Area Network (SAN)
- Enterprise Private Network (EPN)
- Passive Optical Local Area Network (POLAN)
Q.15) Name the different types of network topologies and brief their advantages?
Answer: Network Topology is nothing but the physical or logical way in which the devices (like nodes, links, and computers) of a network are arranged. Physical Topology means the actual place where the elements of a network are located.
Logical Topology deals with the flow of data over the networks. A link is used to connect more than two devices of a network. And more than two links located nearby form a topology.
Network topologies are classified as below:
a) Bus Topology: In Bus Topology, all the devices of the network are connected to a common cable (also called as the backbone). As the devices are connected to a single cable, it is also termed as Linear Bus Topology.
The advantage of bus topology is that it can be installed easily. And the disadvantage is that if the backbone cable breaks then the whole network will be down.
b) Star Topology: In Star Topology, there is a central controller or hub to which every node or device is connected through a cable. In this topology, the devices are not linked to each other. If a device needs to communicate with the other, then it has to send the signal or data to the central hub. And then the hub sends the same data to the destination device.
The advantage of the star topology is that if a link breaks then only that particular link is affected. The whole network remains undisturbed. The main disadvantage of the star topology is that all the devices of the network are dependent on a single point (hub). If the central hub gets failed, then the whole network gets down.
c) Ring Topology: In Ring Topology, each device of the network is connected to two other devices on either side which in turn forms a loop. Data or Signal in ring topology flow only in a single direction from one device to another and reaches the destination node.
The advantage of ring topology is that it can be installed easily. Adding or deleting devices to the network is also easy. The main disadvantage of ring topology is the data flows only in one direction. And a break at a node in the network can affect the whole network.
d) Mesh Topology: In a Mesh Topology, each device of the network is connected to all other devices of the network. Mesh Topology uses Routing and Flooding techniques for data transmission.
The advantage of mesh topology is if one link breaks then it does not affect the whole network. And the disadvantage is, huge cabling is required and it is expensive.
Q .16) Define Static IP and Dynamic IP?
Answer: When a device or computer is assigned a specified IP address then it is named as Static IP. It is assigned by the Internet Service Provider as a permanent address.
Dynamic IP is the temporary IP address assigned by the network to a computing device. Dynamic IP is automatically assigned by the server to the network device.
Q .17) Define SMTP(simple mail transfer protocols)?
Answer:
SMTP
- SMTP stands for Simple Mail Transfer Protocol.
- SMTP is a set of communication guidelines that allow software to transmit an electronic mail over the internet is called Simple Mail Transfer Protocol.
- It is a program used for sending messages to other computer users based on e-mail addresses.
- It provides a mail exchange between users on the same or different computers, and it also supports:
- It can send a single message to one or more recipients.
- Sending message can include text, voice, video or graphics.
- It can also send the messages on networks outside the internet.
- The main purpose of SMTP is used to set up communication rules between servers. The servers have a way of identifying themselves and announcing what kind of communication they are trying to perform. They also have a way of handling the errors such as incorrect email address. For example, if the recipient address is wrong, then receiving server reply with an error message of some kind.
Components of SMTP
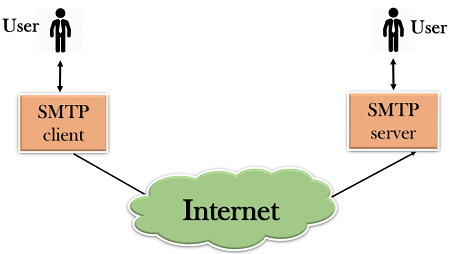
- First, we will break the SMTP client and SMTP server into two components such as user agent (UA) and mail transfer agent (MTA). The user agent (UA) prepares the message, creates the envelope and then puts the message in the envelope. The mail transfer agent (MTA) transfers this mail across the internet.
Q .18) What is difference between unicast broadcast and multicast?
Answer:
Unicast: traffic, many streams of IP packets that move across networks flow from a single point, such as a website server, to a single endpoint such as a client PC. This is the most common form of information transference on networks.
Broadcast: Here, traffic streams from a single point to all possible endpoints within reach on the network, which is generally a LAN. This is the easiest technique to ensure traffic reaches its destinations.
This mode is mainly utilized by television networks for video and audio distribution. Even if the television network is a cable television (CATV) system, the source signal reaches all possible destinations, which is the key reason that some channels’ content is scrambled. Broadcasting is not practicable on the public Internet due to the massive amount of unnecessary data that would continually reach each user’s device, the complications and impact of scrambling, and related privacy issues.
Multicast: In this method traffic recline between the boundaries of unicast (one point to one destination) and broadcast (one point to all destinations). And multicast is a “one source to many destinations” way of traffic distribution, which means that only the destinations that openly point to their requisite to accept the data from a specific source to receive the traffic stream.
Q .19) Define IP Address class and range?
Answer:
TCP/IP defines five classes of IP addresses:
Class A IP addresses are used for huge networks, like those deployed by Internet Service Providers (ISPs). Class A IP addresses support up to 16 million hosts (hosts are devices that connect to a network (computers, servers, switches, routers, printers…etc.) and a Class A network can be divided into 128 different networks.
Class B IP addresses are used for medium and large-sized networks in enterprises and organizations. They support up to 65,000 hosts on 16,000 individual networks.
Class C addresses are most common and used in small business and home networks. These support up to 256 hosts on each of 2 million networks.
Class D and E addresses are least used. Class D is reserved for a not widely used, and reserved for special cases largely for services and applications to stream audio and video to many subscribers at once. Class E addresses are reserved for research purposes by those responsible for Internet networking and IP address research, management, and development.
Classes of IP addresses are:
For the IP addresses from Class A, the first 8 bits (the first decimal number) represent the network part, while the remaining 24 bits represent the host part. For Class B, the first 16 bits (the first two numbers) represent the network part, while the remaining 16 bits represent the host part. For Class C, the first 24 bits represent the network part, while the remaining 8 bits represent the host part.
Q .20) Difference between IPV4 VS IPV6?
Answer:
| Basis for differences | IPv4 | IPv6 |
|---|---|---|
| Size of IP address | IPv4 is a 32-Bit IP Address. | IPv6 is 128 Bit IP Address. |
| Addressing method | IPv4 is a numeric address, and its binary bits are separated by a dot (.) | IPv6 is an alphanumeric address whose binary bits are separated by a colon (:). It also contains hexadecimal. |
| Number of header fields | 12 | 8 |
| Length of header filed | 20 | 40 |
| Checksum | Has checksum fields | Does not have checksum fields |
| Example | 12.244.233.165 | 2001:0db8:0000:0000:0000:ff00:0042:7879 |
| Type of Addresses | Unicast, broadcast, and multicast. | Unicast, multicast, and anycast. |
| Number of classes | IPv4 offers five different classes of IP Address. Class A to E. | lPv6 allows storing an unlimited number of IP Address. |
| Configuration | You have to configure a newly installed system before it can communicate with other systems. | In IPv6, the configuration is optional, depending upon on functions needed. |
| VLSM support | IPv4 support VLSM (Variable Length Subnet mask). | IPv6 does not offer support for VLSM. |
| Fragmentation | Fragmentation is done by sending and forwarding routes. | Fragmentation is done by the sender. |
| Routing Information Protocol (RI P) | RIP is a routing protocol supported by the routed daemon. | RIP does not support IPv6. It uses static routes. |
👍------------Best of luck-------------👍
Now here most common full form of computer networking
**********************************************
Given link below👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇










Comments
Post a Comment